SINUSITIS
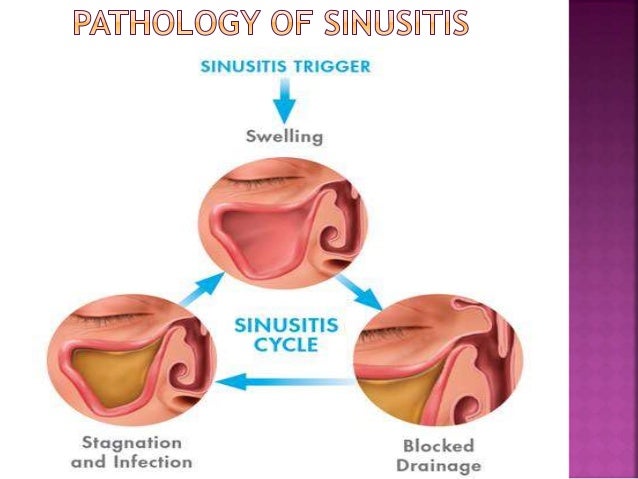
- It is the acute inflammation of the sinus mucosa
- Most commonly involved sinus is maxillary sinus(ethmoid>frontal>sphenoid sinuses)
ETIOLOGY
- BACTERIOLOGY
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus infuenzae
- Moraxella Catarrhalis
- Streptococcus pyogenes,
- Satphylococcus aureus,
- Klebsiella pneumoniae,
- Anaerobic infections are seen in sinusitis of dental origin
EXCITING CAUSES
- Nasal infection: viral rhinitis followed by bacterial invasion.
- Swimming and diving: infection water enters sinuses through ostia.
- Trauma : Compound fractures or penetrating injuries.
- Dental infections.
PREDISPOSING CAUSES
- Obstruction to sinus ventilation and drainage ( DNS,hypertrophic turninates, polyp,edema of ostia, neoplasms, edema of ostia).
- Stasis of secretions in nasl cavity( Cystic fibrosis,enlarged adenoids, choanal atresia)
- Previous attacks of sinusitis
- Environment: cold and wet climate.
- Poor general helth: Exanthematous fever( measles, chickenpox).nutritional deficiences, systemic disorders.
PATHOLOGY
Acute Maxillary sinusitis:
- AETIOLOGY
- Dental infections (periapical dental abscess, orontral fistula)
- Viral rhinitis followed by bacterial invasion.
- Diving and swimming.
- Trauma (fractures and penetrating injuries)
- Clinical features:
- Constitutional symptoms.
- pain.
- Rdness and edema of cheek.
- Postnasal discharge
DIAGNOSIS:
- Xray: WATER'S VIEW
- CT is preferred
- Anterior Nasal Endoscopy
TREATMENT
- MEDICAL
- Antimicrobial drugs(ampicillin/amoxicillin/erythromycin)
- Nasal decongestant drops( 0.1%oxy or xylometazoline).
- Steam inhalation.
- Analgesics
- Hot fomentation.
- SURGICAL
- Antral lavage
ACUTE ETHMOIDAL SINUSITIS
- AETIOLOGY
- Associated with infection of other sinuses.
- CLINICAL FEATURES
- Pain
- Oedema or lids
- Nasal discharge (middle or superior meatus).
- Swelling of the middle turbinate.
DIAGNOSIS
- Xray: WATER'S VIEW
- CT is preferred..
- Anterior Nasal Endoscopy
- An allergy test
- History and Examination
TREATMENT
- MEDICAL
- Antimicrobial drugs( ampicillin/ amoxicillin/erythromycin)
- Nasal decongestant drops(0.1% oxy or xylometazoline)
- Steam inhalation
- Analgesics to relieve pain
- Hot fomentation
- SURGICAL
- Antral lavage
ACUTE ETHMOIDAL SINUSITIS
- AETIOLOGY
- Associated with infection of other sinuses
- CLINICAL FEATURES
- Pain
- Oedema of lids
- Nasal discharge(middle or superior meatus)
- Swelling of the middle turbinate.
DIAGNOSIS
- Computer tomography
TREATMENTS
- Medical treatments same as for acute maxillary sinusitis.
- In case of posterior orbit abscess, drainage of ethmoid sinuses into nose through external ethmoidectomy incision may be requires.
CHRONIC SINUSITIS
- It is the sinus infection lasting for months or years
- Important causes is failure of acute infection to resolve
Clinical Features:
Similar to acute sinusitis but of lesser severity.
Purulent nasal discharge is the commonest complaints.
Foul smelling discharge (anerobic infection)
Local pain and tenderness are not marked.
Nasal stuffiness and anosmia (in some patients).
DIAGNOSIS
- Xray (musosal thickening)
- Xray with contrast
- CT
- Aspiration(pus is confirmatory)
TREATMENT
- Cause for obstruction of sinus drainage and ventilation to be found out.
- Work up on nasal allergy my be required.
- Culture and sensitivity (selection of antibiotic).
- Conservative management (antibiotics, decongestants,antihistaminics)
SURCIACAL TREATMENT
- CHRONIC MAXILLARY SINUSITIS
- Antral puncture and irrigation
- Intranasal antrostomy
- Caldwell-IUC operation
- CHRONIC ETHMOIDAL SINUSITIS
- Intranasl ethmoidectomy
- External ethmoidectomy
TYPES :
- Xray: WATER'S VIEW
- CT is preferred
- Anterior Nasal Endoscopy
TREATMENT
- MEDICAL
- Antimicrobial drugs(ampicillin/amoxicillin/erythromycin)
- Nasal decongestant drops( 0.1%oxy or xylometazoline).
- Steam inhalation.
- Analgesics
- Hot fomentation.
- SURGICAL
- Antral lavage
ACUTE ETHMOIDAL SINUSITIS
- AETIOLOGY
- Associated with infection of other sinuses.
- CLINICAL FEATURES
- Pain
- Oedema or lids
- Nasal discharge (middle or superior meatus).
- Swelling of the middle turbinate.
DIAGNOSIS
- Xray: WATER'S VIEW
- CT is preferred..
- Anterior Nasal Endoscopy
- An allergy test
- History and Examination
TREATMENT
- MEDICAL
- Antimicrobial drugs( ampicillin/ amoxicillin/erythromycin)
- Nasal decongestant drops(0.1% oxy or xylometazoline)
- Steam inhalation
- Analgesics to relieve pain
- Hot fomentation
- SURGICAL
- Antral lavage
ACUTE ETHMOIDAL SINUSITIS
- AETIOLOGY
- Associated with infection of other sinuses
- CLINICAL FEATURES
- Pain
- Oedema of lids
- Nasal discharge(middle or superior meatus)
- Swelling of the middle turbinate.
DIAGNOSIS
- Computer tomography
TREATMENTS
- Medical treatments same as for acute maxillary sinusitis.
- In case of posterior orbit abscess, drainage of ethmoid sinuses into nose through external ethmoidectomy incision may be requires.
CHRONIC SINUSITIS
- It is the sinus infection lasting for months or years
- Important causes is failure of acute infection to resolve
Clinical Features:
Purulent nasal discharge is the commonest complaints.
Foul smelling discharge (anerobic infection)
Local pain and tenderness are not marked.
Nasal stuffiness and anosmia (in some patients).
DIAGNOSIS
- Xray (musosal thickening)
- Xray with contrast
- CT
- Aspiration(pus is confirmatory)
TREATMENT
- Cause for obstruction of sinus drainage and ventilation to be found out.
- Work up on nasal allergy my be required.
- Culture and sensitivity (selection of antibiotic).
- Conservative management (antibiotics, decongestants,antihistaminics)
SURCIACAL TREATMENT
- CHRONIC MAXILLARY SINUSITIS
- Antral puncture and irrigation
- Intranasal antrostomy
- Caldwell-IUC operation
- CHRONIC ETHMOIDAL SINUSITIS
- Intranasl ethmoidectomy
- External ethmoidectomy





0 Comments
If you have any question regarding this post, please let me know.